by Claire Taylor
Dr Gemma McDonald, Sophie Jones, Gloria Odongo, Dr Sara Day.Chelsea & Westminster Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Background
New HIV diagnoses in England are higher among heterosexuals (49%) than gay/bisexual men (GBMSM)(45%). 40% are late-stage diagnoses.
BASHH recommends annual HIV testing for high-risk populations including people who inject drugs (PWID), sex workers and GBMSM. There is limited guidance around frequency of HIV testing among heterosexuals, with some data suggesting less than annual testing.
We analysed historical HIV testing activity among heterosexuals newly diagnosed with HIV via SHL to inform future testing intervals amongst this population.
Method
Electronic notes of heterosexuals newly diagnosed HIV+ by SHL between 8/1/18–19/11/22
were reviewed.
Demographics, prior sexual health clinic attendance and HIV testing activity were collected from SHL triage forms (completed by service user) and telephonic discussions with the SHL clinical team who disclosed the HIV result to the user.
Results
53 new HIV+ diagnoses were identified: median age 33.8yrs (range 18–62yrs); 26 (49%) female, 27 (51%) male; 29 (54.7%) UK born and 24 (45.3%) born overseas.
29 (54.7%) individuals reported a previous HIV test, 17 had never tested and in seven it wasn’t documented.
Of those with prior HIV tests:
Nine (16.9%) tested using SHL, a median 32.5wks ago (range 2.4wks–80.5wks): Seven (77.7%) and two (22.2%) individuals had tested within 12mths and more than 12mths ago respectively.
21 (39.6%) individuals tested elsewhere, of median 15mths ago (range 2days–15yrs): Eleven (52.4%) and ten (47.6%) individuals had tested within 12mths and more than 12mths ago respectively.
28 (52.8%) heterosexuals reported prior clinic attendance, and five (47.2%) reported they had never attended a clinic.
Ten (18.9%) heterosexuals reported recent condomless sex, necessitating PEP discussions with partners.
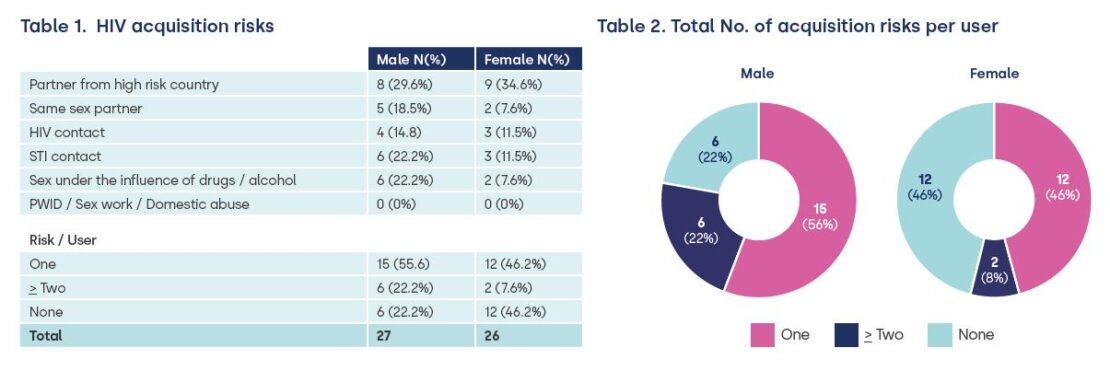
Acquisition risks are shown in Table 1 and 2. Discrepant risk information, between the triage form and SHL telephone discussion, was reported in 24.5% (n=13) with some denying the risks they had cited on their triage form whilst others disclosed new risks at the telephone discussion.
Discussion
Over half of heterosexuals reported a previous HIV testing history before their HIV diagnosis. 32% (17/53) of individuals
had tested within 12mths.
Almost 50% women and 20% men had no discernible acquisition risk and 25% provided inconsistent information about their risks during the testing process.
If SHL had limited HIV testing amongst heterosexuals to yearly/less or based on service user-reported risks, eleven (20.7%) individuals could have experienced a missed/delayed HIV diagnosis or risked onward transmission.
Further research is required to guide HIV testing intervals in heterosexuals accessing sexual health services.



About the author:
Claire is the Senior Digital Marketing Executive at Preventx.